Difference between Price Action, Momentum and Market Breadth
Price action refers to the movement of a security's price over time. It is a key aspect of technical analysis, and traders often use price charts to identify trends, support and resistance levels, and other patterns that can provide insight into the security's likely future price movements.
Momentum is a measure of the strength or velocity of price movement. There are several momentum indicators that traders can use to measure momentum, including the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) and the Relative Strength Index (RSI). These indicators can help traders identify whether a security's price is gaining or losing momentum and whether it is overbought or oversold.
Market breadth refers to the number and strength of securities participating in a market trend. For example, if a broad market index (such as S&P 500) is rising, but only a small number of stocks are driving the increase, it could be a sign of weakness in the overall market trend. Conversely, if a large number of stocks are participating in the trend, it could be a sign of strength. Traders can use market breadth indicators, such as the Advance/Decline Line, to track market breadth and assess the overall health of the market.
In summary, price action is a measure of a security's price movement, momentum is a measure of the strength of that movement, and market breadth is a measure of the number and strength of securities participating in a market trend.
Trading
Trading Edge
Develop a trading process to build an edge in order to become a consistently profitable, well-disciplined trader.
A trading edge involves applying price action techniques like candlesticks and chart patterns, as well as technical indicators, to spot confluences at key levels on multi-timeframe charts.
Include a discretionary criteria in your trading edge to adapt to current market conditions.
To manage your money and risk effectively, use position sizing and stop-loss orders to protect your capital.
Effective trade management can help to maximize profits, minimize losses, and improve the overall performance of your trades. Knowing when to enter/exit and increase/decrease the quantity of your positions is key.
Long-term success in trading requires discipline and self-awareness, so maintaining the right trading psychology is critical. Don't let your emotions cloud your decision-making. Trading can be stressful, and emotions such as fear, greed, or hope can easily influence your decisions. Be aware of your emotions while remaining objective. No impulse trading and No random trades.
Trading is about continuous learning, so review your trades, make a list of your mistakes, and work to fix them every day.
Here are some steps you can take to find your trading edge:
Define your goals and risk tolerance. Clearly identifying your goals and risk tolerance will help you to
determine the types of trades that are most appropriate for you.
Develop a trading plan. A trading plan should outline your entry and exit points, position sizing, risk
management, and any other key elements of your trading strategy.
Conduct thorough market research. Use both technical and fundamental analysis to gather information about the
market and the instruments you are trading.
Identify your unique perspective or advantage. This could be a particular trading style, a specialized knowledge
of a particular market or instrument, or a unique approach to risk management.
Test and refine your edge. Use backtesting or paper trading to test your edge and see how it performs in
different market conditions. Continuously monitor and evaluate your results and make adjustments as needed.
Here are some additional ways you can enhance your trading edge:
Stay up to date with market news and developments. This can help you to anticipate market moves and make
informed trading decisions.
Consider using multiple time frames when analyzing the market. This can help you to get a more comprehensive
view of the market and spot confluences on different time frames.
Use multiple technical indicators. Don't rely on just one indicator, as different indicators can provide
different insights into market trends and conditions.
Be open to learning from other traders. Seek out traders with different styles and approaches and consider
incorporating some of their techniques into your own trading.
Use risk management tools such as stop-loss orders and position sizing to minimize potential losses and protect
your capital.
Stay disciplined and stick to your trading plan. Don't let emotions cloud your judgment or cause you to deviate
from your strategy.
Remember, finding and maintaining your trading edge is an ongoing process that requires discipline, hard work,
and a willingness to learn and adapt.
Trading Edge
Structure Based Trading
Structure-based trading is a method of trading that involves analyzing the underlying structure of financial markets to identify potential buying or selling opportunities. This approach can be used in a variety of financial markets, including stocks, futures, options, and currencies.
Here are some steps you can follow to learn structure-based trading:
Understand the basics of technical analysis: Technical analysis is the study of market trends and patterns, using tools such as charts, indicators, and oscillators. A basic understanding of technical analysis is essential for structure-based trading, as it helps you identify key levels of support and resistance, trend direction, and other important factors that can impact your trades.
Learn about chart patterns: Chart patterns are specific formations that can occur on a price chart, and they can provide insight into the underlying market trend and potential buying or selling opportunities. Some common chart patterns include head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, and triangles.
Learn about trendlines: Trendlines are lines drawn on a chart to connect a series of price highs or lows, and they can help you identify the direction and strength of a trend. Understanding how to draw and interpret trendlines is an important part of structure-based trading.
Practice your skills: The best way to learn structure-based trading is to practice analyzing charts and making trades using a practice account or a low-risk trading platform. This will allow you to hone your skills and build your confidence in your trading strategy.
Educate yourself: There are many resources available to help you learn structure-based trading, including books, courses, and online tutorials. It's important to continue learning and staying up-to-date with the latest techniques and strategies to improve your trading skills.
Trading
Trading Psychology
Trading psychology refers to the mental and emotional aspects of trading, including the thoughts, feelings, and
behaviors that can affect a trader's decision-making process. It's an important aspect of trading because it can
have a significant impact on a trader's success or failure.
Some key considerations in trading psychology include:
Confidence: Confidence is important in trading because it allows you to make decisions with clarity and
conviction. However, too much confidence can lead to overconfidence, which can cause traders to make risky or
impulsive decisions.
Discipline: Discipline is the ability to stick to a plan and not deviate from it, even in the face of
temptations or setbacks. It's important in trading because it allows traders to make consistent, rational
decisions based on their strategy rather than being swayed by emotions.
Emotional control: Emotional control is the ability to manage and regulate your emotions, particularly in
high-stress situations. It's important in trading because emotions can lead to impulsive decisions that may not
be in line with a trader's strategy.
Patience: Patience is the ability to wait for the right opportunities to arise rather than acting
impulsively. It's important in trading because it allows traders to be selective about their trades and not
succumb to the pressure to make trades just for the sake of making them.
Risk management: Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risk in trading.
It's important in trading because it allows traders to protect their capital and manage their losses.
Developing good trading psychology requires a combination of self-awareness, self-discipline, and the ability to
manage and regulate your emotions. It can be a challenging process, but it is essential for long-term success in
trading.
Few tips, tricks, and hacks on Trading Psychology
Trading psychology can be a challenging aspect of trading, as it involves managing emotions and staying focused and disciplined. Here are a few tips, tricks, and hacks for improving trading psychology:
Set clear trading goals and objectives: Having clear goals and objectives can help you stay focused and motivated, and can also help you measure your progress and adjust your approach as needed.
Develop a trading plan: A trading plan should include specific rules for when to enter and exit trades, as well as risk management strategies. Following a plan can help you stay disciplined and avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions.
Practice risk management: Proper risk management is crucial for long-term success in trading. This includes setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and not over-leveraging your account.
Take breaks: Trading can be mentally and emotionally exhausting, so it's important to take breaks and give your mind and body a chance to rest and recharge.
Seek guidance and support: If you're struggling with trading psychology, consider seeking guidance from a mentor or joining a trading community for support and advice.
Keep a trading journal: Keeping a record of your trades and your thoughts and emotions during the process can help you identify patterns and areas for improvement in your trading psychology.
By following these tips and tricks, you can improve your trading psychology and increase your chances of success as a trader.
Improving Your Psychology
Improving your psychology involves working on your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors to become a happier and more fulfilled person. Here are a few tips for improving your psychology:
Practice self-care: Taking care of your physical and mental health is important for overall well-being. This might include things like exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and eating a healthy diet.
Cultivate positive relationships: Building and maintaining positive relationships with friends, family, and loved ones can have a big impact on your overall well-being.
Set and work towards goals: Having goals can give you a sense of purpose and direction, and the process of working towards them can be rewarding and fulfilling.
Practice gratitude: Focusing on the things you are grateful for can help you cultivate a positive outlook and improve your overall well-being.
Seek support: If you're struggling with your psychology, it can be helpful to seek support from a therapist or counselor. They can help you work through any challenges you might be facing and provide you with strategies for improving your psychology.
By following these tips and making a conscious effort to improve your psychology, you can become a happier and more fulfilled person.
Trading Psychology
Explain Price Action?
Price action is the movement of a security's price over time, as reflected in its price chart. Price action analysis involves studying the price movements of a security, typically using charts, to identify trading opportunities.
Price action analysis can be used in conjunction with technical indicators, but it can also be used on its own. It is based on the idea that the market's price reflects all relevant information and that past price movements can help to predict future price movements.
Price action traders look for patterns and trends in the price chart that can indicate buying or selling opportunities. These patterns can include things like breakouts, reversals, and continuations.
Price action traders also pay attention to key levels of support and resistance, which are areas on the chart where the price has had difficulty breaking through in the past. These levels can act as barriers to further price movement and can indicate potential turning points in the market.
It is important to note that price action analysis is just one aspect of technical analysis, and it should be used in conjunction with other tools and techniques in order to get a complete picture of the market.
Raw Price Action
Raw price action refers to the movement of a security's price over time, without the use of any technical indicators or other data overlays. Instead, it relies on the basic supply and demand dynamics of the market to determine the direction and magnitude of price movements.
Traders who use raw price action as a trading approach often focus on identifying key support and resistance levels, trend lines, and chart patterns in the price action. These traders may also use fundamental analysis to evaluate the underlying economic and financial factors that could impact the security's price.
One advantage of using raw price action is that it can help traders identify key levels of support and resistance that may not be immediately apparent when using technical indicators. It can also be a useful approach for traders who are looking to develop a more intuitive understanding of the market and the underlying factors that drive price movements.
Here are a few books that focus on raw price action in the financial markets:
"The Naked Trader" by Robbie Burns: This book provides a comprehensive overview of price action trading and covers a wide range of topics, including technical analysis, risk management, and psychology. It is suitable for traders of all levels and provides practical advice and real-world examples.
"Price Action Trading: The Ultimate Guide" by Dave Manley: This book is a comprehensive guide to price action trading, covering everything from the basics of technical analysis to advanced trading strategies. It includes numerous examples and case studies to help traders apply the concepts to real-world situations.
"Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets" by John J. Murphy: This is a classic book on technical analysis that covers a wide range of topics, including price action analysis, chart patterns, and indicators. It is suitable for both beginner and advanced traders and includes numerous examples and case studies.
"The Candlestick Course" by Steve Nison: This book is a comprehensive guide to candlestick charting, which is a popular way to analyze price action. It covers the basics of candlestick charting as well as more advanced concepts, and includes numerous examples and case studies.
"The Complete Guide to Market Breadth Indicators" by Gregory Morris: This book covers a wide range of market breadth indicators, which are technical indicators that measure the strength of the overall market. It includes chapters on various types of market breadth indicators, including advance-decline lines and the Arms Index, and provides practical guidance on how to use them in trading.
Here are a few tips and tricks for trading using raw price action:
Keep it simple: Don't try to overcomplicate things. Focus on the basics of price action analysis, such as support and resistance levels, trendlines, and chart patterns.
Use multiple time frames: Don't rely on just one time frame. Instead, use multiple time frames to get a better sense of the overall trend and look for confluence between different time frames.
Use stops and take profits: Protect your trades by using stop-loss orders to limit your potential losses and take-profit orders to lock in your profits.
Use risk management: Don't risk more than you are comfortable losing on any single trade. Use position sizing and risk management techniques to protect your capital.
Stay disciplined: Don't let your emotions get the best of you. Stick to your trading plan and be disciplined in your decision-making.
Keep a trading journal: Record your trades and analyze your performance to identify what works and what doesn't. This will help you refine your trading strategy and improve your results over time.
Don't overtrade: Avoid the temptation to make too many trades. It's better to be selective and wait for high-quality setups rather than trying to force trades.
By following these tips and tricks, you can improve your results and increase your chances of success in trading using raw price action.
Price Action
My Trading Plan
A trading plan is a detailed set of guidelines that outlines how you will approach trading. It should include your goals, risk management strategies, and the specific rules and criteria that you will use to make buy and sell decisions. Having a trading plan can help you make consistent, rational decisions and keep your emotions in check.
Here are the steps you can follow to build a trading plan:
Define your goals: What do you want to achieve with your trading? Do you want to make a certain amount of money, or are you more interested in the intellectual challenge of trading? Understanding your goals will help you tailor your trading plan to your specific needs.
Determine your risk tolerance: How much risk are you willing to take on in your trades? This will help you determine the appropriate size of your positions and set appropriate stop-loss orders.
Identify your market and time frame: What type of assets will you be trading (stocks, futures, forex, etc.), and on what time frame (day trading, swing trading, long-term investing)? This will help you determine the appropriate strategies and techniques to use in your trading.
Develop your entry and exit strategies: How will you determine when to enter and exit trades? Will you use technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both? Make sure to include specific criteria and rules that you will use to make these decisions.
Create a risk management plan: How will you manage risk in your trades? Will you use stop-loss orders, position sizing, or a combination of both? Make sure to include specific rules and guidelines for risk management in your plan.
Test and review your plan: Once you have developed your trading plan, it's important to test it and review it regularly. This will help you refine your plan and make any necessary adjustments based on your performance and the market conditions.
Trading Plan
What is Momentum in Trading?
Momentum in trading refers to the rate at which the price of a security is changing over a particular time period. A security with a high momentum is generally experiencing rapid price movements, while a security with a low momentum is experiencing slower price movements.
Traders often use momentum indicators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI)and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), to measure the strength of a security's price trend. These indicators can help traders identify whether a security is overbought (experiencing a sustained uptrend) or oversold (experiencing a sustained downtrend), which can be used as potential buy or sell signals.
For example, a trader who sees a stock with a strong upward momentum might decide to buy the stock, hoping that the upward trend will continue. On the other hand, a trader who sees a stock with a downward momentum might decide to sell the stock, hoping to avoid any further price declines.
Momentum can be a useful tool for traders who are looking to enter or exit a trade at an opportune time. However, it is important to note that momentum can change quickly, and it is just one factor to consider when making trading decisions. It is always a good idea to use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis and to carefully consider the broader market context before making any trades.
Trading Momentum
Market Breadth Simplified
Market breadth is a measure of the overall direction of the stock market. It is used to assess the strength of the market and to identify potential trends.
There are several ways to measure market breadth, but one common method is to look at the number of stocks that are advancing versus the number of stocks that are declining. A market with a high breadth is considered to be strong, as it indicates that a large number of stocks are moving in the same direction. A market with a low breadth is considered to be weak, as it indicates that fewer stocks are participating in the trend.
Market breadth can also be measured by looking at the number of stocks that are trading above or below certain price levels, such as their moving averages (e.g. 200 EMA) or key support and resistance levels.
Traders and investors use market breadth as one tool among many to assess the overall health of the market and to identify potential buying or selling opportunities. It is important to note that market breadth is just one aspect of market analysis, and it should be used in conjunction with other tools and techniques in order to get a complete picture of the market.
Market Breadth
Which are the most used trading indicator?
There is no single most used trading indicator, as different traders have different preferences and use different indicators to suit their individual trading strategies. Some commonly used indicators include Moving Averages (SMA, EMA), Pivot Points (PP, S1, S2, R1, R2), Bollinger Bands, MACD, VWAP and the Relative Strength Index (RSI). These indicators can be used to identify trends, measure volatility, and identify potential buy or sell signals. It is important to note that no single indicator is perfect, and it is often best to use a combination of indicators in order to get a more comprehensive view of the market. It is also important to backtest and validate any indicator before using it in live trading.
Trading Indicators
What are the reversal trading setups in an uptrend?
There are several reversal trading setups that can be used in an uptrend:
Double top or double bottom: This is a chart pattern in which the price creates two peaks at approximately the same level, creating a resistance level. If the price breaks through this resistance level, it could indicate a potential trend reversal.
Head and shoulders: This is a chart pattern that consists of a left shoulder, a head, and a right shoulder. If the price breaks through the neckline, it could indicate a potential trend reversal.
Bullish or bearish divergences: These occur when the price of an asset is making new highs or lows, but the corresponding indicator (such as the RSI) is not. This could indicate that the trend is losing momentum and may be ready to reverse.
Breakout and breakdown: A breakout occurs when the price breaks through a resistance level, while a breakdown occurs when the price breaks through a support level. These events can sometimes signal a trend reversal.
It is important to note that these are just a few examples and that traders should be aware of the risks and limitations of relying on any single indicator or setup. It is always a good idea to use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis and to carefully consider the broader market context before making any trading decisions.
Trading Reversals
Trading Setups
Trading Uptrend
What are the reversal trading setups in a downtrend?
There are several reversal trading setups that traders can look for in a downtrend. Here are a few examples:
Bullish divergence: This is when the price of a security is making lower lows, while an oscillator (such as the RSI or MACD) is making higher lows. This divergence suggests that the selling pressure may be weakening, and a reversal to an uptrend could be imminent.
Double bottom: This is a chart pattern that forms when the price of a security bounces off a support level twice, creating two distinct lows. If the price then breaks above the neckline (the line connecting the highs between the two bottoms), it could signal a reversal to an uptrend.
Bullish engulfing pattern: This is a two-candle pattern in which the second candle completely covers the body of the first candle. If this pattern appears after a downtrend, it could signal that buyers are taking control of the market and a reversal to an uptrend is likely.
It's important to note that these reversal setups are not guaranteed to work, and traders should always use them in conjunction with other technical and fundamental analysis techniques to confirm their validity.
Trading Reversals
Trading Setups
Trading Downtrend
How to manage your RISK in Trading?
There are several risk management techniques that day traders can use to help protect their capital and minimize potential losses:
Set stop-loss orders: A stop-loss order is an order to sell a security when it reaches a certain price, which is typically below the current market price. This helps limit potential losses by selling the security before it falls further in value. This can help to minimize losses if the market moves against you.
Use risk-reward ratios: When setting up a trade, consider the potential reward relative to the potential risk. For example, you might aim for a risk-reward ratio of 1:3, meaning that you are willing to risk 1 unit in order to potentially gain 3 units. Risk-reward ratios help traders assess the potential risk and reward of a trade and make informed decisions about whether to enter or exit a position.
Use position sizing: Position sizing refers to the size of a trade relative to the trader's account balance. By carefully managing position size, traders can ensure that any individual trade does not have an outsized impact on their account balance. (to avoid drawdowns)
Diversify the portfolio: Diversification helps spread risk across multiple assets and asset classes, which can help protect against significant losses in any one area.
Use risk management tools: There are a variety of tools available to help traders manage risk, including stop-loss orders, trailing stop orders, and risk-reward ratio calculators. Hedging with other derivatives such as options, futures, and margin. It is important to understand how these tools work and to use them appropriately.
Keep emotions in check: It can be easy to get caught up in the excitement of trading, but it is important to remain disciplined and stick to your risk management plan.
Continuously assess and adjust: Risk management is an ongoing process. Regularly review your trades and adjust your risk management plan as needed to ensure that it remains effective.
It's important to note that no risk management technique is foolproof, and traders should always be aware of the potential for loss when trading. It's also essential to have a clear understanding of one's own risk tolerance and to never risk more capital than one can afford to lose.
Risk Management
Risk:Reward Trader
A risk-reward trader is a trader who focuses on the potential risk and reward of a trade in order to make informed decisions about whether to enter or exit a position. This approach involves assessing the potential loss that could be incurred if the trade does not go as planned (the risk), as well as the potential profit that could be gained if the trade is successful (the reward).
Risk-reward traders typically use risk-reward ratios to help them assess the potential risk and reward of a trade. For example, if a trader is considering a trade that has a potential risk of $100 and a potential reward of $200, the risk-reward ratio would be 2:1 (200/100). This means that the potential reward is twice the size of the potential risk, which may make the trade attractive to the trader.
Risk-reward traders often aim to enter trades where the potential reward is significantly larger than the potential risk, as this can help increase the chances of profitability over time. However, it's important to note that no trade is guaranteed to be successful, and traders should always be prepared for the possibility of losses.
Trend Analysis
Trend analysis is a technique used in technical analysis to identify the direction and strength of a market trend. A trend is a general direction in which the market is moving over a specific period of time, and it can be either up (bullish), down (bearish), or sideways (range-bound).
There are several tools and techniques that traders can use to analyze trends, including:
Trend lines: These are lines drawn on a chart to connect successive high or low points, and they can help traders identify the direction and strength of a trend.
Moving averages: These are averages of a security's price over a specific period of time, and they can help traders identify trends and gauge the strength of a trend.
Trend indicators: These are technical indicators that are specifically designed to identify trends, such as the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) and the Average Directional Index (ADX).
Price patterns: These are recurring patterns that can occur on a price chart, such as head and shoulders or double tops, and they can provide insight into the direction and strength of a trend.
Trend analysis is an important aspect of technical analysis and can help traders identify opportunities to buy or sell a security based on its likely future price movements. It's important to note, however, that trends can change over time, and it's important to continually monitor market conditions and adjust trading strategies accordingly.
Multi-Timeframe Chart Analysis
Using multiple timeframes is a technique that involves analyzing a security or market on different timeframes in order to get a more comprehensive view of its price action. For example, a trader might look at a daily chart to get a sense of the long-term trend, a 4-hour chart to identify intermediate-term trends, and a 15-minute chart to identify short-term trends.
There are several benefits to using multiple timeframes in trading:
It can provide a more complete picture of a security's price action: By looking at a security on different timeframes, traders can get a sense of its overall trend as well as any shorter-term price fluctuations.
It can help confirm trends and patterns: By looking at a security on multiple timeframes, traders can confirm that a trend or pattern is present on multiple timeframes, which can increase the likelihood that it is a valid signal.
It can help identify potential entry and exit points: By looking at a security on multiple timeframes, traders can identify potential entry and exit points that align with the trends on each timeframe.
It can help reduce risk: By using multiple timeframes, traders can better manage their risk by identifying potential entry and exit points that align with the trends on different timeframes.
Using multiple timeframes can be a useful tool for traders looking to get a more comprehensive view of a security's price action. It's important to note, however, that different timeframes can present different perspectives on a security, and it's important to carefully consider all relevant information when making trading decisions.
Skills required to become a Profitable Trader?
There are several skills that can be helpful for becoming a profitable trader in the stock market:
Market knowledge: A good trader should have a deep understanding of the markets they are trading, including the underlying factors that can affect the prices of the securities they are trading.
Risk management: Trading involves risk, and a good trader should be able to manage that risk effectively in order to minimize potential losses. This includes using tools such as stop-loss orders and position sizing to control risk.
Analytical skills: A good trader should be able to analyze market data and make informed decisions based on that analysis. This includes using technical and fundamental analysis techniques to identify trading opportunities and assess market trends.
Discipline: Trading can be emotionally challenging, and it is important for a trader to be disciplined and stick to their trading plan even in the face of market volatility or unexpected events.
Adaptability: Markets are constantly changing, and a good trader should be able to adapt to new market conditions and adjust their trading strategy as needed.
Patience: Trading can be a long-term game, and it is important for a trader to be patient and not get caught up in the short-term fluctuations of the market.
It is also important for a trader to continually educate themselves and stay up to date on market trends and developments. This can help them to stay on top of their game and make informed trading decisions.
Top 10 Swing Trading Strategies
Swing trading is a trading strategy that involves holding positions for a period of a few days to a few weeks in an attempt to profit from short-term price movements. Here are ten swing trading strategies that traders may consider:
Trend following: This involves identifying a trend in the market and riding it by buying or selling in the direction of the trend.
Breakout trading: This involves identifying key levels of support and resistance and buying or selling as the price breaks through these levels.
Mean reversion: This involves buying or selling after the price has moved too far in one direction, with the expectation that it will eventually return to its mean or average value.
Candlestick patterns: This involves using specific candlestick chart patterns, such as dojis and spinning tops, to identify potential trade setups.
Moving average crossover: This involves using two moving averages with different time frames and buying or selling when they cross over.
Oscillator divergence: This involves using oscillators, such as the RSI, to identify potential trend reversals based on divergences between the oscillator and the price.
Gap and go: This involves buying a stock that has a price gap from the previous day's close and selling it for a quick profit.
News trading: This involves buying or selling based on market-moving news events
High relative strength: This involves buying stocks that are outperforming the overall market and selling those that are underperforming.
Range trading: This involves buying or selling as the price approaches the top or bottom of a defined range.
It is important to note that no single strategy is perfect, and traders should carefully consider their own goals and risk tolerance before choosing a swing trading strategy. It is also important to backtest and validate any strategy before using it in live trading.
Top 10 intra-day trading strategies
Intraday trading involves holding positions for a relatively short period of time, typically within a single trading day, in an attempt to profit from short-term price movements. Here are ten intraday trading strategies that traders may consider:
Scalping: This involves taking quick profits on small price movements, typically holding positions for just a few minutes or even seconds.
News trading: This involves buying or selling based on market-moving news events.
Range trading: This involves buying or selling as the price approaches the top or bottom of a defined range.
Breakout trading: This involves identifying key levels of support and resistance and buying or selling as the price breaks through these levels.
Mean reversion: This involves buying or selling after the price has moved too far in one direction, with the expectation that it will eventually return to its mean or average value.
Candlestick patterns: This involves using specific candlestick chart patterns, such as dojis and spinning tops, to identify potential trade setups.
Moving average crossover: This involves using two moving averages with different time frames and buying or selling when they cross over.
Oscillator divergence: This involves using oscillators, such as the RSI, to identify potential trend reversals based on divergences between the oscillator and the price.
Momentum trading: This involves buying or selling based on the strength of the price trend, as measured by indicators such as the RSI.
High relative strength: This involves buying stocks that are outperforming the overall market and selling those that are underperforming.
It is important to note that no single strategy is perfect, and traders should carefully consider their own goals and risk tolerance before choosing an intraday trading strategy. It is also important to backtest and validate any strategy before using it in live trading.
High Profitability and Probability Trading Strategies
There are many different trading strategies that can be profitable, and the best strategy for you will depend on your individual goals and risk tolerance. Some strategies that tend to have a high probability of success include:
Trend following: This involves identifying a trend in the market and then trading in the same direction as the trend. This can be done using technical analysis tools such as moving averages or trendlines.
Dollar cost averaging: This involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the price. This can help to reduce the impact of market volatility and can be a good strategy for long-term investors.
Position trading: This involves holding onto a trade for a longer period of time, typically several weeks or months. This can be a good strategy for traders who are able to accurately forecast long-term market trends.
Mean reversion: This involves identifying assets that are trading at extreme levels and then buying or selling them in anticipation of a return to their historical average.
It's important to note that no trading strategy is foolproof and all strategies carry some level of risk. It's always important to do your own research and carefully consider your own financial goals and risk tolerance before making any trading decisions.
Creating Trading bias & time frame alignment
Creating a trading bias and aligning it with a specific time frame is a technique that involves developing a general outlook on the market or a specific security and identifying the time frame that aligns with that outlook.
For example, a trader who has a bullish bias on a particular stock might look for opportunities to buy that stock on a daily or weekly time frame, as these time frames align with their long-term outlook for the stock. On the other hand, a trader who has a bearish bias on a particular stock might look for opportunities to sell that stock on a shorter-term time frame, such as a 15-minute chart, as this time frame aligns with their shorter-term outlook for the stock.
There are several benefits to creating a trading bias and aligning it with a specific time frame:
It can help traders focus on the time frame that aligns with their outlook: By aligning their bias with a specific time frame, traders can focus on opportunities that align with their outlook for the market or a specific security.
It can help reduce risk: By focusing on a specific time frame, traders can better manage their risk by aligning their trades with the trends on that time frame.
It can help increase the likelihood of successful trades: By focusing on a specific time frame that aligns with their outlook, traders can increase the likelihood of success by trading in the direction of the overall trend on that time frame.
It's important to note that a trading bias and time frame alignment are just one aspect of trading, and traders should always be prepared for the possibility of losses and carefully consider all relevant information when making trading decisions.
Price Fractals
Price fractals are a concept in technical analysis that refers to repeating patterns in the price action of a security or market. Fractals are characterized by a specific pattern of price highs and lows that repeat over different time frames.
Fractals are typically identified by a series of five price bars, with the middle bar being the highest or lowest in the series. The two bars on either side of the middle bar must be lower (in the case of a high fractal) or higher (in the case of a low fractal) than the middle bar, and the final two bars on either end must be higher (in the case of a high fractal) or lower (in the case of a low fractal) than the middle bar.
Fractals can be used in a variety of ways in technical analysis, including identifying potential support and resistance levels and identifying potential trend reversal points. It's important to note, however, that fractals are just one tool among many that traders can use to analyze the market, and they should be used in conjunction with other technical and fundamental analysis techniques.
Important candlestick patterns
Candlestick charts are a type of chart that is commonly used in technical analysis to visualize the price action of a security. Each candlestick on the chart represents the range of price movement for a specific period of time, with the body of the candlestick representing the open and close prices and the wicks representing the high and low prices.
There are several important candlestick patterns that traders may use to identify potential trading opportunities:
Bullish and bearish engulfing patterns: These patterns occur when a small candlestick is completely engulfed by a larger candlestick of the opposite color. A bullish engulfing pattern occurs when the small candlestick is bearish (black or red) and the larger candlestick is bullish (white or green), indicating a potential trend reversal to the upside. A bearish engulfing pattern occurs when the small candlestick is bullish and the larger candlestick is bearish, indicating a potential trend reversal to the downside.
Dojis: A doji is a candlestick with a small body and long wicks, indicating that the open and close prices were almost equal. Dojis can indicate indecision in the market and may be a sign of a potential trend reversal.
Hammer and hanging man: A hammer is a candlestick with a small body and a long lower wick, indicating that the price tried to move lower but ultimately ended up closing near the open price. A hanging man is similar but occurs at the top of an uptrend. These patterns can indicate a potential trend reversal to the downside.
Morning and evening stars: These patterns consist of three candlesticks, with the first being a small body candle, the second being a large body candle, and the third being a small body candle of the opposite color. A morning star occurs at the bottom of a downtrend and indicates a potential trend reversal to the upside, while an evening star occurs at the top of an uptrend and indicates a potential trend reversal to the downside.
It is important to note that candlestick patterns should not be used in isolation, and it is always a good idea to use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis and to carefully consider the broader market context before making any trading decisions.
How to identify potential entry and exit points in trading?
There are a few key strategies that traders use to identify potential entry and exit points for day trading. Here are a few of them:
Technical analysis: This involves using charts and other technical indicators to identify patterns and trends that may indicate a good time to buy or sell a security.
Fundamental analysis: This involves evaluating the underlying financial and economic factors that may affect the value of a security, such as earnings, dividends, and economic indicators.
News and events: Traders may also consider news and events that may affect the value of a security, such as earnings announcements, regulatory changes, and geopolitical developments.
Support and resistance levels: These are price levels at which a security has historically had difficulty breaking through and may indicate potential entry or exit points.
Personal risk tolerance: It's also important to consider your personal risk tolerance when identifying entry and exit points. You should only enter a trade if you are comfortable with the potential loss and have a clear plan for how you will exit the trade if it doesn't go as expected.
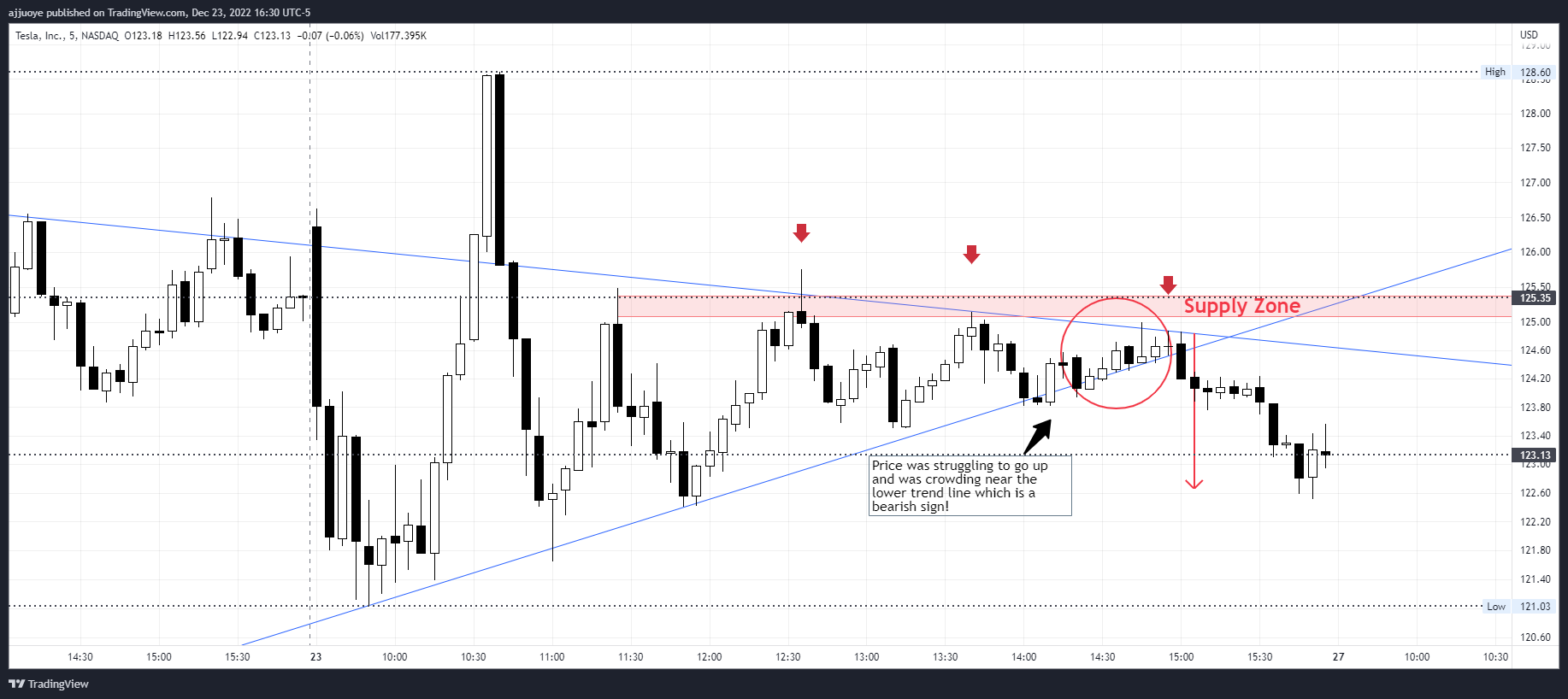
Understanding the Quality of Zones & Pace of Move
The quality of zones and pace of move are two concepts in technical analysis that can be used to assess the strength and likelihood of a trend continuing.
The quality of zones refers to the level of support or resistance that a specific price level provides. For example, a price level that has been tested multiple times and has consistently held as a support or resistance level would be considered a high-quality zone. On the other hand, a price level that has only been tested once or twice and has not consistently held as a support or resistance level would be considered a low-quality zone.
The pace of move refers to the speed at which a market is moving in a specific direction. A market that is moving quickly in a specific direction may be considered to have a strong pace of move, while a market that is moving slowly or sideways may be considered to have a weak pace of move.
Understanding the quality of zones and pace of move can be useful for traders in assessing the likelihood of a trend continuing and identifying potential entry and exit points. It's important to note, however, that these concepts are just one aspect of technical analysis and should be used in conjunction with other technical and fundamental analysis techniques.
How to improve your concentration to enhance your trading?
Improving concentration can be challenging, especially in today's fast-paced and distraction-filled world. Here are a few tips for improving concentration:
Set specific goals: Having specific goals can help you stay focused and motivated. Make a list of the tasks you want to complete, and try to work on one task at a time until it is finished.
Minimize distractions: Remove or minimize any distractions that might interrupt your concentration, such as turning off your phone or finding a quiet place to work.
Take breaks: It's important to take breaks and give your mind a chance to rest. Taking breaks can actually improve your concentration, as it allows your brain to recharge and come back to tasks with renewed energy.
Exercise and get enough sleep: Exercise and getting enough sleep can help improve your concentration and overall cognitive function.
Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment. Practicing mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, can help improve your concentration and focus.
By following these tips and making them a part of your daily routine, you can improve your concentration and focus, which can help you be more productive and successful in your personal and professional endeavors.
Tips for improving Decision Making in Trading
Decision making is an important skill that can impact many aspects of our lives, from our personal relationships to our careers. Here are a few tips for improving decision making:
Identify the problem or decision to be made: Before making a decision, it's important to clearly identify the problem or decision that needs to be made. This can help you focus your efforts and make a more informed decision.
Gather information: To make a good decision, it's important to gather as much relevant information as possible. This might include researching options, consulting with experts, or seeking input from others.
Consider the consequences: Think about the potential consequences of each possible decision, both short-term and long-term. This can help you weigh the pros and cons of each option and make a more informed decision.
Use a decision-making framework: There are various decision-making frameworks that can help guide your decision making process. One example is the Pareto principle, which suggests that you should focus on the most important 20% of the options that will yield 80% of the desired results.
Seek feedback: After making a decision, seek feedback from others to see if there were any aspects that you may have missed or if there are any improvements that can be made in the future.
By following these tips and making decision making a conscious process, you can improve your decision-making skills and make better decisions in your personal and professional life.
Using VWAP & Keltner Channels for enhancements with ORB
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) is a technical analysis indicator that shows the average price at which a security has traded over a given time period, based on both volume and price. It is often used as a benchmark for the price of a security, or as a reference point for traders to determine if a security is overbought or oversold.
Keltner channels are a technical analysis tool that uses three exponential moving averages (EMAs) to create a channel around the price action of a security. The upper and lower bands of the Keltner channel are based on the average true range (ATR), which is a measure of volatility. The center line of the Keltner channel is typically a 20-period EMA of the security's price.
One way to use VWAP and Keltner channels together is to look for price action that diverges from the VWAP and approaches or breaks through the upper or lower Keltner channel. This could indicate a potential trend change or overbought/oversold condition.
ORB (Opening Range Breakout) is a trading strategy that involves identifying the range of price movement in a security during the first few minutes of trading, and then entering a trade if the price breaks out of that range in either direction. Some traders use VWAP and Keltner channels as enhancements to the ORB strategy by using them as additional reference points for determining entry and exit points for trades.
It's important to note that technical analysis tools like VWAP and Keltner channels are only one aspect of trading, and should be used in conjunction with other fundamental and technical analysis techniques. It's also important to have a solid risk management plan in place and to thoroughly research and understand the security or market you are trading before making any investment decisions.
Trading Decisions
Trading decisions refer to the choices made by traders as they analyze and evaluate market conditions in order to decide whether to buy, sell, or hold a particular security. These decisions are based on a variety of factors, including technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and the trader's risk tolerance and investment objectives.
Traders use a variety of tools and techniques to help them make informed trading decisions, including charts, indicators, and fundamental data such as company financial statements and economic reports. It's important for traders to carefully consider all available information before making a trade, as market conditions can change rapidly and the potential for profit or loss is always present.
It's also important for traders to have a clear plan in place for managing risk, including setting stop-loss orders and diversifying their portfolio to minimize the impact of any individual trade.
Enhancing Patience for Trading
Patience is an important virtue in trading, as it allows traders to make more informed and thought-out decisions rather than reacting impulsively to market movements. Impulsiveness can be a significant risk in trading, as it can lead to making rash and poorly thought-out decisions that can result in financial losses. Here are some tips for avoiding impulsiveness and practicing patience in trading:
Set clear trading goals and objectives: Having a clear idea of what you want to achieve through trading can help you stay focused and avoid making impulsive decisions.
Use stop-loss orders: Stop-loss orders allow you to set predetermined exit points for your trades, which can help you manage risk and avoid making rash decisions based on short-term market movements.
Use a trading journal: Keeping a record of your trades and the thought process behind them can help you reflect on your decision-making process and identify any areas where you may be prone to impulsive behavior.
Take breaks: Trading can be mentally and emotionally exhausting, so it's important to take breaks and step away from the markets to clear your mind.
Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness is the practice of being present and fully aware in the moment. Engaging in mindfulness exercises, such as meditation or yoga, can help you cultivate patience and improve your ability to handle stress.
It's important to remember that developing patience takes time and practice. It's normal to struggle with impatience at times, but by consistently working on building this skill, you can improve your trading discipline and decision-making.
It's important to also remember that impulsiveness is a natural tendency that can be difficult to overcome. However, by consistently working on building self-control and discipline, you can improve your ability to avoid impulsive decisions in trading.
Most Common Trading Mistakes
There are many common mistakes that traders can make, both novice and experienced. Here are a few examples:
Trading on emotions: It's important to approach trading with a clear and rational mind, rather than making decisions based on emotions such as greed, fear, or hope.
Lack of a trading plan: Having a well-defined trading plan can help traders stay disciplined and avoid making impulsive decisions. A trading plan should include a clear set of entry and exit rules, as well as a risk management strategy.
Failing to diversify: It's important to diversify a trading portfolio to spread risk across multiple assets and asset classes. This can help protect against significant losses in any one area.
Over-leveraging: Using too much leverage (borrowing money to trade) can significantly increase the potential for losses, as well as the potential for margin calls (when a trader is required to add more money to their account to meet margin requirements).
Ignoring risk management: It's important to have a plan in place to manage risk, including setting stop-loss orders and regularly reviewing positions to ensure they are still in line with the trader's risk tolerance and investment objectives.
Not keeping up with market developments: It's important for traders to stay informed about market news and developments that could affect the securities they are trading. Failing to do so can lead to missed opportunities or unexpected losses.
How to recover from BIG Trading Losses
Recovering from a big trading loss can be difficult, but it's important to remain calm and take a measured approach to getting back on track. Here are a few steps that may be helpful in recovering from a large trading loss:
Take a break: It's important to step back and take some time to process the loss and assess what went wrong. This can help prevent impulsive decisions that could further compound the loss. Think back and write down everything you did to the point how you were feeling and what emotions were incharge was it greed, fear, fomo, fight or flight
Review your trading plan: It may be helpful to review your trading plan, including your risk management plans and assess whether it was properly followed or if any adjustments need to be made. This can help identify any weaknesses in the plan and help prevent similar losses in the future.
Seek guidance: It can be helpful to seek guidance from a mentor or professional trader to help identify any mistakes that were made and to learn from them.
Stay disciplined: It's important to stick to your trading plan and risk management strategy, even when things don't go as planned. This can help prevent further losses and keep you on track to meeting your long-term investment goals.
Keep perspective: It's important to remember that trading involves risk, and losses are a natural part of the process. While it's important to take steps to minimize losses, it's also important to keep things in perspective and not let a single loss define your trading career.
Its is important to understand no matter what your trading plan and strategies are but protecting your capital at all times should be you number one priortiy
Money Management in Trading
Money management in trading refers to the process of effectively managing your trading capital and risk to increase the probability of long-term profitability. It involves setting risk management strategies, such as stop-loss orders and position sizing, to limit potential losses and preserve capital.
Here are some key principles of money management in trading:
Risk management: It is important to manage your risk by setting stop-loss orders and position sizes that are appropriate for your trading capital and risk tolerance. This helps to limit potential losses and protect your capital.
Position sizing: Proper position sizing involves determining the appropriate size of your trades based on your trading capital and the level of risk you are willing to take. It is important to avoid overleveraging, as this can lead to large losses if the trade goes against you.
Diversification: Diversifying your portfolio across different asset classes and markets can help to reduce the overall risk of your portfolio and increase your chances of long-term profitability.
Long-term perspective: Trading should be viewed as a long-term investment rather than a get-rich-quick scheme. It is important to have a long-term perspective and be patient, as consistent profits are often the result of a large number of small wins over time.
Money Management
Trade Management in Trading
Trade management in trading refers to the process of managing your trades from entry to exit. It involves making decisions about when to enter a trade, when to exit, and how to manage your trades in the meantime.
Here are some key elements of trade management:
Trade entry: Trade entry involves deciding when to enter a trade based on your analysis of market conditions and the specific security or commodity you are trading.
Trade management: Once you are in a trade, trade management involves deciding how to manage the trade in the short-term. This can include setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and taking profits at predetermined levels to lock in gains.
Trade exit: Trade exit involves deciding when to exit a trade. This can be based on a variety of factors, such as reaching a predetermined profit target, the trade going against you, or a change in market conditions.
Effective trade management can help to maximize profits, minimize losses, and improve the overall performance of your trades.
Here are some other trade management strategies that traders can use:
Scaling in: Scaling in involves entering a trade with a small position size and gradually increasing the size of your position as the market moves in your favor. This can help to minimize risk and maximize profits.
Scaling out: Scaling out involves gradually selling off a portion of your position as the market moves in your favor. This can help to lock in profits and reduce the overall risk of your position.
Trail stop: A trail stop is a dynamic stop-loss order that is set at a certain percentage or dollar amount below the market price. As the market moves in your favor, the stop-loss order is adjusted to follow the market price, protecting your profits while allowing the trade to continue to run.
Reverse pyramid: A reverse pyramid is the opposite of a pyramid trade. It involves progressively decreasing the size of your position as the market moves in your favor, with the goal of maximizing profits and minimizing risk.
Risk reversal: A risk reversal involves simultaneously selling a call option and buying a put option on the same security or commodity. This can be a way to hedge your position and reduce the overall risk of your trade.
Scaling-in or Pyramid trading is a strategy in which a trader adds to their position as the market moves in their favor. It involves progressively increasing the size of your position as the market moves in your favor, with the goal of maximizing profits.
Here's an example of how pyramid trading might work:
You enter a trade with a small position size.
As the market moves in your favor and the price of the security or commodity increases, you add to your position by purchasing more of the security or commodity.
As the market continues to move in your favor, you add to your position again, increasing the size of your overall position.
You continue to add to your position in this manner until the market reaches a predetermined profit target or until the trend begins to reverse.
The risk with pyramid trading is that if the market moves against you, your losses can be significant. It is important to use proper risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders, to limit potential losses when using this strategy.
Trade Management
Mean Reversion
Mean reversion is a trading strategy that assumes that prices will eventually move back to their average or "mean" level after experiencing an extreme move. It is based on the idea that prices tend to oscillate around a central trend or mean over time, rather than moving in a straight line.
There are several indicators that traders can use to identify mean reversion opportunities. Some common examples include:
Bollinger Bands: These are bands plotted above and below a moving average, with the upper and lower bands representing standard deviations from the mean. When the price moves outside of the bands, it could be a sign that the price is overbought or oversold and may soon revert back to the mean.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): This is a momentum indicator that measures the difference between two moving averages. When the MACD line crosses above or below the signal line, it could indicate a potential mean reversion opportunity.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): This is an oscillator that measures the strength of a security's price action. A reading above 70 is considered overbought, while a reading below 30 is considered oversold. If the RSI moves into one of these extreme levels, it could be a sign that the price is due for a mean reversion.
It's important to note that these indicators should be used in conjunction with other technical and fundamental analysis techniques to confirm mean reversion opportunities.
Mean reversion is a popular trading strategy that is based on the idea that prices will eventually move back to their average or "mean" level after experiencing an extreme move. Here are some pros and cons of using mean reversion in trading:
Pros:
Mean reversion can be a profitable strategy: When prices move to extreme levels, they are often overbought or oversold, which can create opportunities for traders to buy low and sell high.
Mean reversion is based on statistical analysis: There is strong empirical evidence that prices tend to move back to their mean over time, which can give traders confidence in their trades.
Mean reversion can be used in different markets: This strategy can be applied to a variety of markets, including stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies.
Cons:
Mean reversion is not a guarantee: While prices may often revert back to their mean, there is no guarantee that this will happen, and traders could experience losses if the price does not revert.
Mean reversion may not work in all market conditions: This strategy may not be as effective during times of high volatility or when there are significant market trends.
Mean reversion requires a long-term perspective: This strategy involves holding positions for an extended period of time, which may not be suitable for traders who prefer a more short-term approach.
Overall, mean reversion can be a useful tool for traders looking to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations, but it's important to carefully consider the pros and cons before implementing this strategy.